|
MpegRepair™
|
|
Software
Encoding and Repair Utility
|
|
| MpegRepair
is a versatile
MPEG encoding utility designed to both ease the difficulty of MPEG
encoding and assist in the repair of troubled video streams. MpegRepair
is capable of handling HDTV and IMAX video frame sizes.
MpegRepair now includes capablity for inserting the Pan & Scan
info into your existing MPEG Stream. MpegRepair
is composed of four tightly integrated applications: |
|
| High Quality, Flexible
Encoder - MpegRepair produces fixed or variable bit-rate MPEG-1
or MPEG-2 streams and gives the user with the ability to adjust every
important parameter of the encoding process. |
| High Resolution Decoder-
MpegRepair displays full resolution MPEG-1 or MPEG-2, DVD or transport
streams and can store individual frames on a disk for analysis or
transcoding. |
| Stream Analyzer-
MpegRepair provides graphical and textural visibility into MPEG video
streams, encoding decisions and header byte offsets. |
| Video Stream
Manipulator - MpegRepair performs GOP and byte accurate cut,
paste, trim, append and replace functions on trouble video
streams. Beginning or ending segments can be cut or trimmed. |
|
|
|
| MpegRepair Increases
Productivity |
| Repair of an encoded video
stream is eased by the ability to mark in and mark out video
segments, then re-encode and replace the segment without the need
to re-encode the entire stream. The trim and cut functions
enable re-sizing at the beginning or end of a video stream. Insert
enables easy addition and modification of titles and credits at
the beginning or end of the video. |
|
| Pan
& Scan |
| For DVD producers,
whose MPEG Encoder does not insert Pan & Scan info into their MPEG Stream,
MpegRepair can inspect the stream and, if requested, it can insert the Pan
& Scan info into their MPEG stream without a need to re-encode. |
| Scenario |
| Perhaps you've just
encoded a 2-hour movie, and have discovered two sections that are not acceptable.
A scene, at the start of the video, has bad blocks and jitter on title text.
Later, in the middle of the video, a detailed high action scene has turned
into blocks. |
| Using the MpegRepair analyzer,
you advance to the troubled scenes and verify the quality problems frame
by frame. The analyzer presents in text and graphical detail, the original
encoding decisions that have resulted in the problems. With this information,
you now have an idea why the problems have occurred. |
| Next, using the MpegRepair decoder,
you mark the section of badly encoded frames. MpegRepair automatically records
the required splicing information. |
|
| The powerful MpegRepair preprocessing
and encoding engine is next used to re-encode original video frames (or
those frames saved during the decode process). Preprocessing filters can
be applied to problem areas within frames or to the entire video. The MpegRepair
encoding engine allows you to add more or fewer bits to problem areas within
frames. The encoding of the small clip can be accomplished interactively
improving the quality on each pass. And the small size of the problem areas
means that the encoding is accomplished within a few seconds. The resultant
video clip will have the exact length and VBV buffer states so that it can
precisely replace the bad MPEG section. Finally, with the click of the splice
button, MpegRepair will replace the original bad video scene with the new
repaired video. ThatŐs all it takes. |
| Additional
useful tasks MpegRepair can accomplish |
| Transcoding |
Modifying
bit-rate or frame sizes of a MPEG or DVD file |
| Change
audio track |
Extracting
video from a MPEG file for multiplexing with a new audio stream |
| Bitmap
to MPEG |
Converting
a single bitmap or TGA frame to a MPEG sequence for appending tiles
to the beginning of a MPEG stream |
| MPEG Properties
Display |
Displaying
video, audio and system properties |
| Video Compliance |
Highlighting
any encoding problems |
| Change
PID |
Extracting
single video or audio PID from transport stream |
| Cut |
Cutting frames
from within a MPEG stream |
| Trim |
Removing MPEG
headers, user data, or non-MPEG bytes from the start or the end of
a MPEG stream |
| Analyze
|
Exploring
video encoding decisions made in encoding the stream |
|
| MpegRepair
Encoder |
| Variable Bit-rate Encoding |
| MpegRepair provides the ability
to change the encoding bit-rate scene by scene throughout an encoding session.
This capability provides more bits (resulting in higher quality) in scenes
that are more difficult to encode, and fewer bits in those scenes that are
easy to encode. |
| Variable Quantization Encoding: |
| The quantization values, which
determine the amount of compression per encoding block, can also be modified
on a scene basis, frame basis, or sub-frame basis. Predefined or user-defined
quantization tables can be changed on scene or GOP boundaries. Quantization
tables customized for specific bit-rates and encoding complexity are provided
with MpegRepair. These tables can also be used as templates for building
complete custom tables for specific encoding situations. In addition, the
quantization within each frame can be modified to increase or decrease the
amount of data that is discarded in that region. |
| Bit Rate Analysis: |
| The optional analysis pass details
the actual encoding difficulty of the video content. The resultant bit-rate
profile and scene change analysis is printed in a text file and plotted
on a chart. It is not often obvious which scenes are more or less difficult
to encode. The analysis pass provides encoding complexity information. Encoding
complexity, combined with knowledge of the relative importance of each scene,
provides a good guideline for the allocation of bits for the video and graphics
components of a DVD disk. |
| Automatic Scene Change Detection |
| MpegRepair can detect scene
changes throughout a video and force the start of a new encoding block (GOP)
coincident with the new scene. This produces the highest quality video by
keeping the I blocks (MPEG key frames) as far apart as possible. I blocks
consume the largest number of bits. |
| Scene Adaptation: |
| An Edit Decision List (EDL)
file, containing parameters that will be changed throughout the encoding
session and the frames at which the changes occur, is read by MpegRepair.
Variable GOP structures can be specified in this file to support frame accurate
GOP entry points for DVD authoring. Slight or significant quantization adjustments
can be made to user defined areas within user defined frames. MpegRepair
EDL operations include a powerful set of preprocessing options as well.
User defined filters can be applied to selected scenes, frames, or even
to user defined regions within a selected frame! |
| Spliceable Segment Encoding: |
| MpegRepair can encode a segment
or a scene with specified starting and ending buffer states. Segment sizes
can be of any length. This allows scenes or segments to be removed, moved,
and reinserted to create legal MPEG video without re-encoding. This also
prevents buffer overflow or under-flow in DVD jumps between segments. |
| Region or Frame Filtering: |
| User defined or included standard
filters can be applied to a designated region of a specified sequence of
frames. The MpegRepair preprocessing engine can apply the selected filter
inside or outside the user selected region. This feature is used to enhance
a region of interest within frames or to minimize artifacts outside of the
region of interest. |
| Preprocessing: |
| MpegRepair includes extensive
frame resizing and frame conversions in a preprocess operation prior to
MPEG encoding. MpegRepair inputs frames directly from digital disk recorders
and frame grabbers. Preprocessing options include chroma down-sampling from
4:2:2 to 4:2:0, D1 to SIF, VGA to SIF, and SIF or QSIF format conversions.
The output of the preprocess operation can be saved to files or just viewed
without encoding. |
| Closed Caption Insertion: |
| Closed caption data (or any
other data) can be inserted into designated sections of the video stream
in the user data MPEG field. |
| Overlay Mixing: |
| MpegRepair can mix a logo bitmap
or an animation with the underlying MPEG. The logo can be placed in any
location within the MPEG video frame and with any mix level. |
| Enhanced for speed on all
Pentium Processors: |
| Computationally intensive components
of MpegRepair are written in low level code that is optimized for speed
on the Pentium processor and utilizes the dual processing pipes that exist
in the Pentium processors. MpegRepair recognizes workstations that support
the MMX instruction set and utilizes the eight parallel processing pipes
in MMX machines. MpegRepair high level control is written as threads that
take advantage of multiprocessor environments. |
| Batch Mode Operation: |
| Batch mode operation of MpegRepair
provides for automatic encoding of multiple MPEG files and allows interactively
with PixelTools companion products. |
| MpegRepair Decoder |
| Converts virtually any
MPEG file into a sequence of frames |
| Stores frames in BMP,
YUV or TGA formats |
| Uses full
floating point accuracy to produce no decoding errors |
| Decoded sequences can
be re-encoded with different parameters |
| Decodes low profile to
high profile streams |
|
| MpegRepair Analyzer |
| Presents encoding decisions
as graphical overlays. |
| Presents user selectable overlays
of |
| |
Motion vectors:
forward and backward |
| |
Encoding blocks:
I, forward, backward, interpolated, not coded, skipped |
| |
Numerical block
values: M quant value |
|
| Displays 24 Bit color
with image zoom and roam |
| Provides motion compensated
error window |
| Plots reported
and actual buffer states |
| Provides details decoding
of all headers: video, audio, system, transport |
| Stores selected stream
characteristics in a log file |
| Includes detailed Quick
View Stream properties |
| |
|
| MpegRepair Stream Manipulator |
| Provides replace
function that is integrated with the analyzer to identify GOP boundaries
and the encoder to re-encode replacement sections. |
| Provides cut
and paste of MPEG video data at GOP boundaries (as identified in the
analyzer) or at user selected byte offsets |
| Provides trim and append
of all file data at GOP boundaries (as identified in the analyzer)
or at user selected byte offsets |
|
MPEG Encoder
| |
MPEG-1
or MPEG-2 Constant or Variable bit-rate |
| |
Flexible
user adjustments for bit-rate, frame size, profile and level
includes |
| |
Access
to most encoding parameters |
| |
Force quantizations
within regions of frames |
| |
Filter
inside or outside of regions of frames |
| |
Extensive
preprocessing capabilities |
| |
Area
and region filters with user definable filters |
| |
User definable
quantization tables |
| |
Segment
encoding |
| |
Fixed quantization
encoding |
| |
Encodes
from simple to high profile streams |
|
MPEG Decoder
| |
MPEG-1
or MPEG-2 decoding of elementary transport, system, or DVD streams
|
| |
Floating
point precision MPEG decode onto computer monitor window Stores
frames to BMP, TGA, or YUV file formats. |
| |
Separated
elementary video and audio from transport, DVD or system files
|
| |
Decodes
High-Low Profile, and 4:2:0 to 4:2:2 |
| |
|
|
MPEG
Stream Editor
| |
Provides
trim, cut, replace, append and insert operations on GOP segment
boundaries or user selected byte offsets |
| |
Encodes
section to specific buffer endpoints at GOP segment boundaries
to be used with stream operations |
| |
Integrated
with MPEG-2 decoder and segment MPEG-2 encoder |
| |
Accomplishes
instantaneous replacement of segments within huge MPEG files
|
| |
Includes
byte accurate advance stream editing features |
|
| |
|
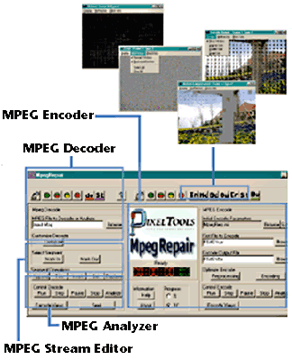
MPEG
Analyzer
| |
Provides a quick
view of MPEG stream properties |
| |
Provides detailed
graphical views, frame by frame, of encoding decisions |
| |
Zoom and roam
on decoding windows |
| |
Displays quantization
and motion vectors |
| |
Decodes user
selectable video and system headers into a text window and into a
log disk file |
| |
Prints any stream
syntax errors in status window and log file |
| |
Plots reported
and actual buffer states |
| |
Records syntax
violation errors in a text window and log file |
|
| Video
Capture Equipment |
Encode
Output |
|
Integrates with all DV boards, frame grabbers, video editors and animation
programs that output AVI format |
|
Inputs
frame from digital disk recorders |
|
| |
Bit-rates
from 1Kbits/sec to 168 Mbits/sec. |
| |
Frame
rates from 1 frame/sec. to 60 frames/sec. |
| |
IPB,
IP, or I-frame only streams |
|
| Encoding
Speed |
| |
Results
of pre-procession without encoding |
|
| |
SIF
format (352x240) 24 frames/sec encoding at 3x real time on Dual Pentium
450 |
| |
D1
format (720x480) 24 frames/sec encoding at 11x real time on Dual Pentium
450 |
| |
|
|
| |
Recommended
bit-rate to log file in analysis mode |
| |
List
of detected scene changes to scene change file |
| |
Encoding
statistics to log file |
| |
Current
parameter configuration |
|
| Operating Systems |
Decoding |
| |
Runs
under WindowsNT, Windows95, Windows98 |
| |
Manages
files larger then 8 Gbytes |
|
| |
Precise
floating point computations with 24-bit color accuracy |
| |
Inputs
MPEG 1 or 2 bitstreams |
|
| Processor |
| |
Stores
frames as YUV, TGA, or BMP files |
|
| |
Runs
on any 386 or greater processor |
| |
Optimized,
MMX and Dual processor |
|
| |
Decodes
elementary systems processing transports or VOB files |
|
| Encode Input
|
Analysis |
| |
BMP,
YUV, Y-U-V, TGA, AVI, DIB, D1, ABEKAS, and PPM |
| |
Fields
and frames in sizes from 16x16 to 16384 x 16384 pixels |
| |
Single
frame or frame sequence to produce a longer stream |
| |
Sequences
stored on multiple drives |
| |
Output
of files from other programs or drag and drop |
| |
Initialization
file containing session specific parameters |
| |
EDL
file describing scene by scene parameters |
| |
Scene
Change file containing known scene changes |
|
| |
24-bit
color frame windows with zoom and roam |
| |
Frames
and fields visible at input, motion compensated, DCTed, compressed,
and error states |
| |
Graphic
windows displaying buffer fullness and encoding statistics |
| |
Motion
vectors, block decision types, quantization values |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Encode
Preprocessing |
User Help Facilities |
| |
Standard
or user defined 7x7 kernel filters |
| |
Full
frame or regional filtering |
| |
D1,
VGA, or SIF downsampling |
| |
Logo
or graphic animation mixing with video |
| |
Video
or graphics RGB conversion |
| |
Half D1 to D1 upsampling |
|
| |
Fly-over
Hints-Comprehensive |
| |
Users
Manual with expert encoding hints |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Encoding |
|
| |
High,
Main, and Low Level encoding |
| |
High,
Main, and Simple Profile encoding |
| |
Optional
MPEG-2 transport packetizing |
| |
8-11
bit selectable DC precision |
| |
Zig-Zag
and Alternate DCT scan |
| |
Dual
Prime, 16x16, and 16x8 field and frame motion estimation |
| |
Temporal
down-sampling to 1 frame per second |
| |
Adjustable
IPB frame patterns (ie, M and N values) |
| |
Selectable
sequence header insertion rates |
| |
Modifiable
start time code |
| |
Target
decoder buffer sizes from 1 to 1000 vbv |
| |
Constant
bit-rate or constant quantization |
| |
4:2:2
and 4:2:0 Chroma formats |
| |
Compresses
from 16x16 to 16384 x 16384 pixel frame sizes |
| |
Supports
all 18 HDTV formats |
| |
Scene by scene bit-rate change capability |
| |
Automatic
or manual GOP forcing |
| |
Segment
encoding to specified buffer states |
| |
Encoding
precision control |
| |
Operator
control of regional quantization within selected frames |
| |
Closed
caption text insertion |
| |
Complete control over encoding precision to optimize session for highest
quality or highest encoding speed |
|
|